Uncover the truth behind 5 Blood Pressure Myths that could be putting your health at risk. From symptoms to medication, learn expert-backed facts on managing hypertension effectively. Get accurate readings with our map calculator blood pressure formula.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- High blood pressure often has no symptoms—it’s called the “silent killer.”
- It’s not just for older people; young adults can have it too.
- Cutting salt alone isn’t enough to control it.
- Family history raises your risk—but doesn’t decide your fate.
- Stopping your medicine without your doctor’s advice can be dangerous.
Knowing the truth helps you make smart choices for your heart. Check your pressure regularly, live a healthy lifestyle, and talk to your doctor.
Introduction
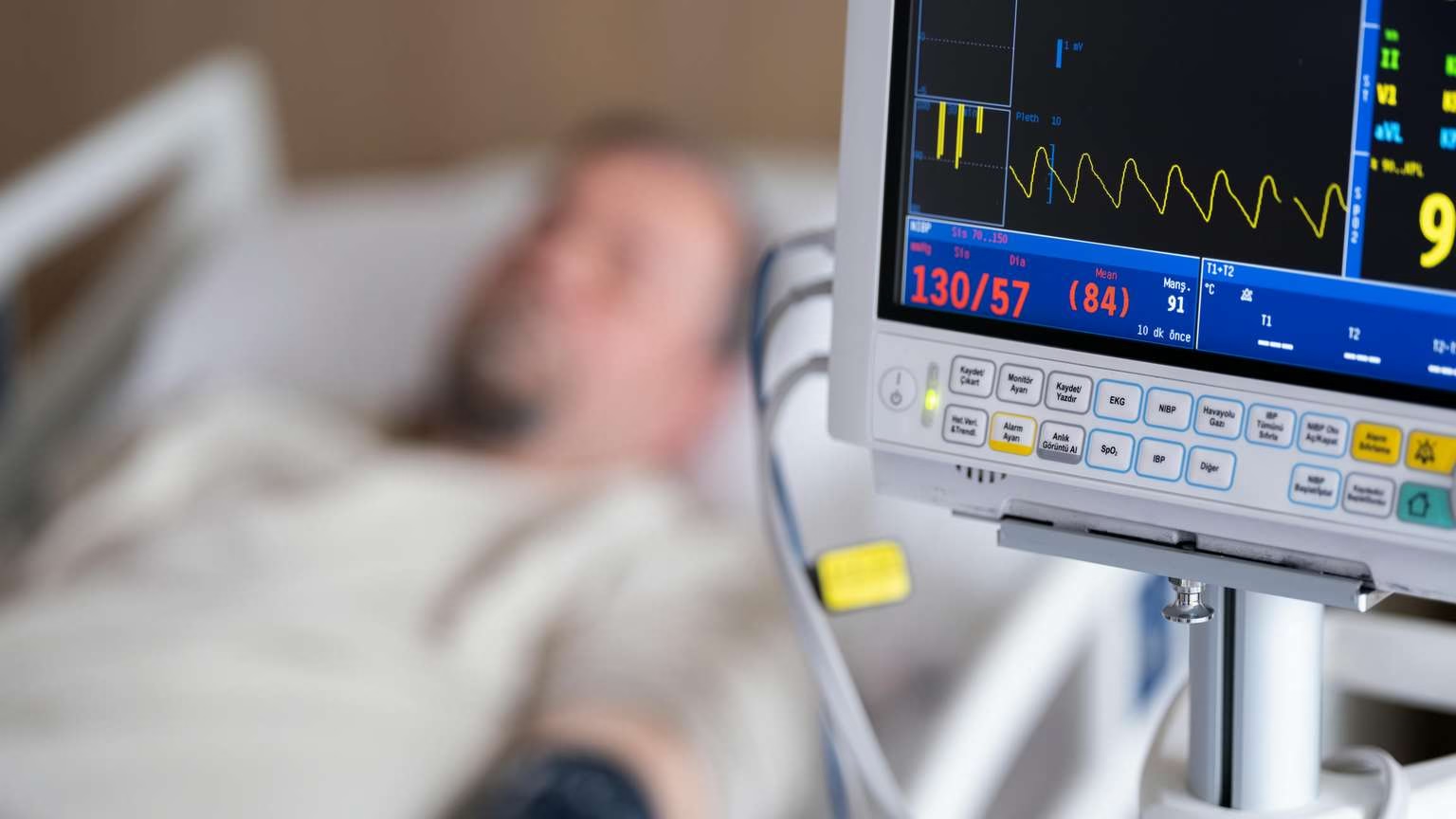
You feel fine—no headaches, no dizziness. But during a routine checkup, your doctor says your blood pressure is high. This happens to millions every year.
High blood pressure, often called the “silent killer,” can damage your body without showing clear signs. Nearly half of adults have it, yet many still believe myths that stop them from getting proper care.
As a blood pressure specialist, I see how these myths delay treatment. This guide clears up five common myths about high blood pressure with real facts and simple actions you can take to protect your heart.
Myth 1: You’ll Always Feel Symptoms if Your Blood Pressure Is High
Why People Believe This
Many people think high blood pressure causes obvious symptoms like headaches or nosebleeds. While extremely high levels can sometimes cause these, most people feel nothing at all.
The Real Facts
High blood pressure usually causes silent damage over time—hurting your arteries, heart, kidneys, and brain before any symptoms appear.
By the time you notice a problem, it could already be serious.
What You Should Do
- Check Often: Don’t wait for warning signs. Get your blood pressure checked at least once a year—or more often if you’re at risk.
- Use a Home Monitor: Check twice a day and share your readings with your doctor.
Forget this myth: regular checks could save your life.
Myth 2: Only Older People Get High Blood Pressure
The Truth About Age
While risk does increase with age, high blood pressure affects people of all ages—including young adults.
Studies show more than 1 in 4 people aged 18–39 already have high blood pressure. Poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress are major factors.
How to Protect Yourself
- Start Early: Even young people should check their blood pressure regularly—especially if they have diabetes or a family history of hypertension.
- Build Healthy Habits Now:
- Exercise at least 150 minutes per week.
- Eat fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit processed foods and manage your weight—losing even 2 pounds can make a difference.
- Special Cases: Women using birth control or who had pregnancy-related high blood pressure are at higher risk later.
Don’t wait until you’re older. Protect your heart today.
Myth 3: If It Runs in the Family, You Can’t Prevent It
Why This Isn’t True
Your genes may raise your risk—but they don’t seal your fate. Your daily habits have a powerful impact.
How to Take Control
- Eat Smart: Follow the DASH diet—low in sodium, rich in potassium (found in bananas, spinach, and potatoes).
- Move Daily: 30 minutes of activity a day—walk, swim, or do yoga.
- Manage Stress & Sleep: Poor rest and chronic stress raise blood pressure. Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep.
- Watch Your Weight: Even small weight loss can lower your numbers.
You’re not powerless. Your lifestyle choices can rewrite your health story.
Myth 4: Cutting Salt Is All You Need to Control Blood Pressure
The Full Story
Yes, reducing salt helps—but it’s not enough on its own. Most of the sodium you eat comes from processed foods, not your salt shaker.
A Complete Plan for Control
- Find Hidden Salt: Check labels on bread, pizza, soups, and snacks. Choose fresh foods.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Limit alcohol, caffeine, and sugar. Focus on potassium-rich fruits and veggies.
- Exercise & Manage Stress: Combine healthy food with regular movement and stress control.
- Take Medicine If Needed: Lifestyle changes may not always be enough; follow your doctor’s advice.
Forget the salt-only myth. A full, balanced approach works best.
Myth 5: You Can Stop Your Medicine Once Your Blood Pressure Is Normal
Why This Is Dangerous
Many people stop taking their medicine once their readings look good. But medication controls blood pressure—it doesn’t cure it. Stopping suddenly can cause serious spikes and even emergencies.
Safe Medication Habits
- Follow Directions: Keep taking your medicine unless your doctor advises otherwise.
- Stay in Touch: Regularly share your readings with your doctor.
- Discuss Side Effects: Don’t stop on your own—your doctor can adjust or change your prescription.
- Think Long-Term: Staying on your plan reduces your risk of stroke and heart attack dramatically.
Stay consistent. Managing your blood pressure is a lifelong commitment to your health.
Conclusion
We’ve busted five major myths about high blood pressure.
Here’s what you now know:
- It’s often silent.
- It can affect anyone, young or old.
- Your habits matter more than your genes.
- Salt is only one piece of the puzzle.
- Medicine is a long-term partner in your heart health.
Takeaway: The truth gives you power.
Check your numbers regularly, live a heart-healthy life, and work with your doctor. Small actions today build a stronger, longer life tomorrow.